Recently had Solar Pv installed and can only speak positively of our experience with Genren Uk.
Great lines of communication, high level of product knowledge and professional work, all carried out within agreed timescale.
Discover the efficient way to heat your home.
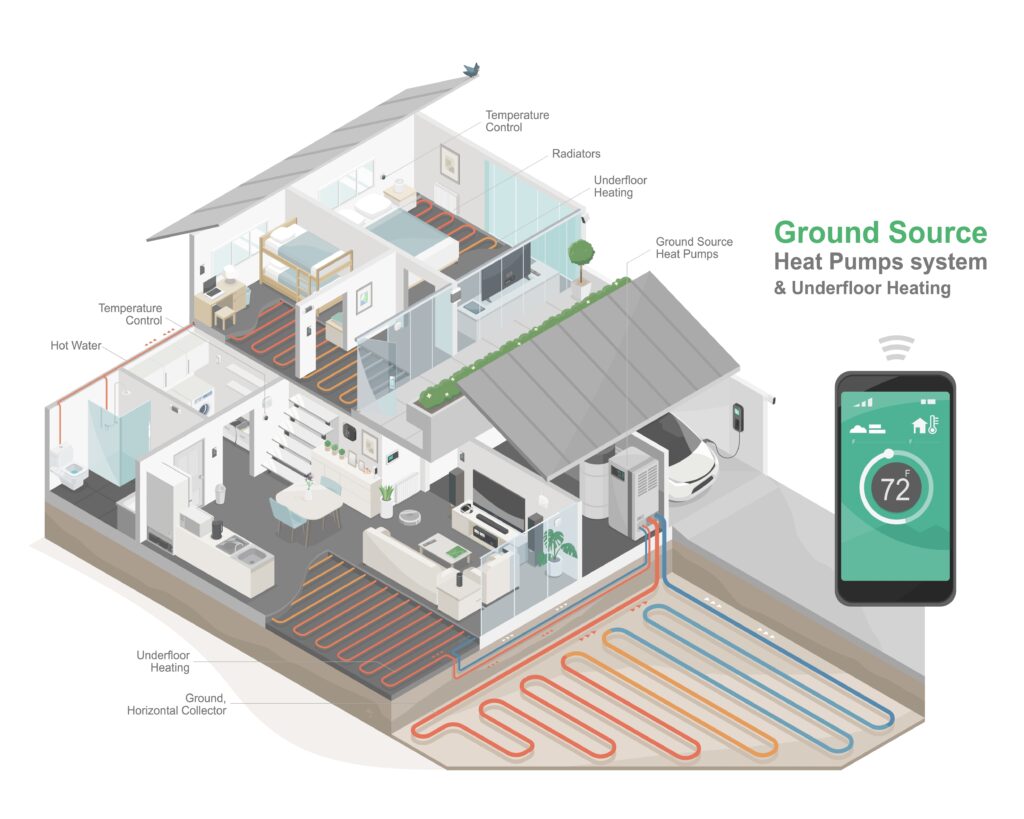
Genren are your trusted professionals for designing and installing high-performance ground source heat pump systems.
With a ground source heat pump, you can capture renewable energy stored naturally beneath your property.
Using the earth’s natural thermal energy to convert heating into hot water for your home. This ground source technology can generate long-term savings on your heating bills, plus reduce your environmental impact.
Ground source heat pumps offer unparalleled efficiency and sustainability for properties with suitable land, providing reliable heating and hot water all year-round.
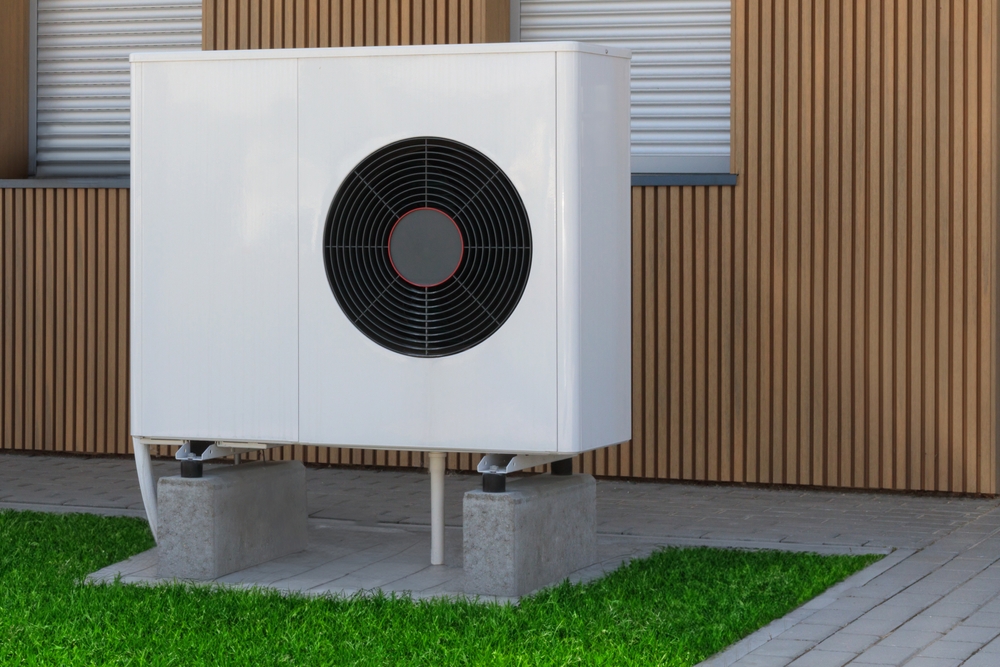

Selecting the right installer is vital for ensuring your air source heat pump operates efficiently and reliably for years to come. At Genren we offer more than just installation; we provide peace of mind.
Every installation is different, but it typically takes between 2-5 days to install an air source heat pump. Our team will work with you to determine the complexity of the installation and provide a guide to timescales before the work begins.
Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHPs) use the earth’s natural, steady underground heat to warm your home. These systems pump a mix of water and heat transfer fluid through buried pipes. This fluid soaks up heat from the ground and groundwater, then carries it back to an indoor unit. There, a smart process of refrigeration and compression boosts the heat’s temperature, making it ready for your home’s heating, like radiators, underfloor heating, or hot water.
GSHPs are remarkably efficient, often achieving efficiencies of 400% or more. This means they deliver at least four units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed, making them a sustainable and cost-effective heating solution year-round, even in the coldest months.
There are two primary ways to install the underground pipes: horizontal trenches, which require significant land but have lower excavation costs, or vertical boreholes, which need much less surface area but involve more specialized and expensive drilling.

Key Benefits of Installing an ASHP
Costs typically range from £20,000 to £55,000+ before the grant, depending on property size, ground conditions, and whether trenches or more expensive boreholes are used.
Access the £7,500 Boiler Upgrade Scheme (BUS) Grant
Make your ASHP installation significantly more affordable! Homeowners in England and Wales replacing fossil fuel systems can get a £7,500 government grant.
We handle the application, and the grant is deducted directly from your cost.
Key Eligibility:
We manage your installation from start to finish, ensuring a smooth transition.
Recently had Solar Pv installed and can only speak positively of our experience with Genren Uk.
Great lines of communication, high level of product knowledge and professional work, all carried out within agreed timescale.
Genren was very professional in their customer service and installation. We even had a phone call afterwards to see if everything was working correctly. It’s great having a local company with a great service.
Extremely happy with service from site survey through to installation. Would highly recommend Genren UK Limited.
I got in touch with Genren to see if my solar system could be improved in its output. They devised a way to do this, planned it, agreed on a date with me and delivered exactly what they promised in exactly the amount of time they said they would.
The improvements allow my panels to deliver their maximum potential. This then revealed problems with the original install which I got Genren to fix. Again they delivered exactly what they said they would, on the date they promised and at 5th price they promised.
In summary I trust them to deliver on quality and value.
From start to finish Genren exceeded our expectations. They answered all of our questions, designed a system that was ideal for our property, and were very tidy when installing our ‘in roof’ solar panels. They kept us informed throughout the whole process and we highly recommend their services to anyone thinking of installing solar on their roof.
Even after only 8 months we’ve significantly reduced our energy bills and we couldn’t be happier.




Find answers to frequently asked questions about the services offered by Genren.
Heat pumps transfer heat from the outside air or ground into your home in winter and reverse the process in summer, providing both heating and cooling.
Modern heat pumps, especially cold-climate models, work effectively in temperatures well below freezing, although efficiency may decrease as temperatures drop significantly.
There are air-source heat pumps, ground-source (geothermal) heat pumps, and water-source heat pumps. Each has different installation needs and efficiencies.
Heat pumps can reduce energy costs by up to 50% compared to traditional heating systems, depending on your local climate and energy rates.
Suitability depends on your climate, current heating system, and energy efficiency of your home. Homes in moderate climates tend to benefit the most.
Heat pumps require regular filter changes and annual professional inspections, but maintenance is relatively low compared to traditional HVAC systems.
Costs vary widely depending on the type of heat pump and complexity of installation, ranging from £14,000 to £20,000 or more.
Yes, a heat pump can replace both a heating system and an air conditioner, as it provides both heating and cooling.
Heat pumps generally last between 10 to 15 years, but their lifespan can be longer with proper maintenance.
Yes, heat pumps are more environmentally friendly compared to fossil fuel heating systems, as they use less electricity and emit fewer greenhouse gases.
Modern ASHPs are quiet, comparable to a fridge. MCS regulations limit noise, and we ensure correct siting.
Yes, they efficiently extract heat even in freezing UK temperatures. Systems are sized for winter conditions.
Usually not in England and Wales, as it’s often ‘permitted development’. We ensure compliance with rules on location and noise. Exceptions apply for listed buildings or conservation areas.
Just enough space outside for the unit (wall-mounted or on the ground) with good airflow around it.
Ready to Switch to Efficient Heating?
Take the first step towards a greener, potentially cheaper way to heat your home. Contact the expert team at Genren today for a free, no-obligation consultation and a bespoke quote tailored to your property. Let us help you access the £7,500 BUS grant and enjoy the benefits of sustainable heating for years to come.
Schedule a consultation or get a free quote